Future of Antimatter Production, Storage, Control, and Annihilation Applications in Propulsion Technologies
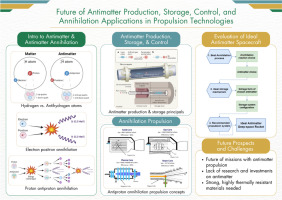
Antimatter propulsion is a groundbreaking technology with potential to transform space exploration, enabling travel to distant locations once deemed impossible. Utilizing antimatter annihilation, this propulsion method boasts an unmatched energy density of 9 × 10¹⁶ J/kg, released with 100% efficiency when antimatter meets matter. Approximately 70% of this energy can be harnessed for propulsion, offering superior efficiency compared to existing technologies, despite some practical losses. Spacecrafts can traverse the Solar System to reach nearby stars in span of days to weeks (within a human lifetime) due to this enormous energy potential. Compared to traditional rocket fuel and nuclear power, antimatter propulsion promises significant environmental benefits by reducing carbon emissions and radioactive waste. However, obstacles including the difficulties of creating, storing, and identifying antimatter have restricted the field’s study and applications. For practical implementation, existing concepts require to be further honed and remain theoretical. The salient features of antimatter generation and storage, as well as the present state of affairs and prospects for revolutionary uses in aerospace engineering, are outlined in this article. Antimatter propulsion is a promising technology that requires more research and development to reach its full potential.



